Cyrus Morrison, MPH, CSCS
Data Analyst | DocSpera
The Data: Lead Times from Booking to Surgery
One of the most important metrics in surgical scheduling is case lead time: the number of days between when a case is booked and when the surgery actually occurs. Looking at total joint surgery data over the past several years, a clear trend emerges:
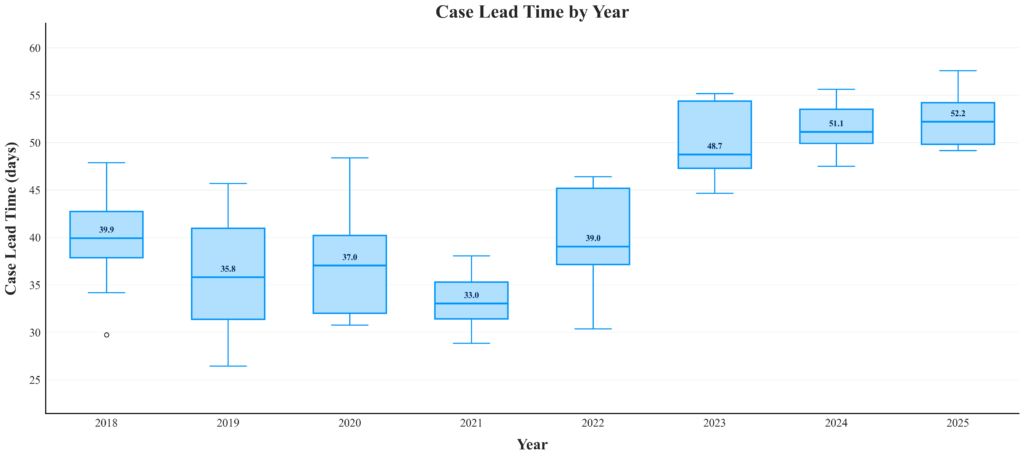
DocSpera examined seven years of arthroplasty scheduling data covering hip, knee, and shoulder procedures from 2018 through mid-2025. After excluding anomalous cases and short-tenure surgeons, the dataset captured 90 months of scheduling behavior, including nearly 80,000 surgeries. While the early years (2018–2021) show relatively stable and even declining lead times, the post-2021 period reveals a sharp and sustained increase. By 2025, the average lead time is over 50 days—a 50% jump compared to 2019.
Why Are Lead Times Rising?
The data tells us what is happening, but not why. Several factors may be contributing to this growing gap between booking and surgery:
1. Increased Patient Volume
- The U.S. population is aging, and with it comes a higher prevalence of arthritis and other degenerative joint conditions.⁷
- Demand for total joint replacement is projected to rise steadily over the next decades.⁷
2. Surgeon Capacity
- While patient demand is rising, the number of practicing orthopedic surgeons has not increased at the same pace.
- Training new surgeons takes years, and retirements may offset growth, creating bottlenecks in access to providers.⁴
3. Operating Room (OR) Time Constraints
- Hospitals and surgery centers have limited ORs and staff availability.
- Competing priorities, such as trauma, oncology, and emergency procedures, reduce block time for elective cases like joint replacements.⁴
- Pandemic-era backlogs may also have lasting ripple effects years later.⁶
4. Hospital and System-Level Pressures
- Staffing shortages among nurses, anesthesiologists, and surgical techs, combined with financial pressures that limit expansion of surgical capacity, have further stressed scheduling flexibility.⁴ ⁶
- Systematic reviews confirm that cancellations and delays in orthopedic surgery are frequently tied to hospital-level constraints.¹ ⁴
- At the same time, advances in digital templating and AI-based planning have demonstrated improved accuracy and efficiency in implant selection, but these gains are most effective when lead times provide adequate runway for preoperative preparation.² ³ ⁵
No single factor is solely responsible; instead, a combination of these elements likely serves as the driving force.
Why It Matters
Longer surgical lead times affect both patients and healthcare systems:
- For patients, extended waiting can worsen pain, limit mobility, and decrease quality of life.⁶
- For providers, delays increase the risk of cancellations, rescheduling headaches, and operational inefficiencies.¹ ⁴ ⁶
- For health systems, rising lead times may indicate misalignment between capacity and demand—an early warning sign for broader access-to-care challenges.¹ ⁶
The Key Question: What Comes Next?
The steady rise in lead times for total joint surgery raises an urgent question:
How can health systems, surgeons, and policymakers align resources to meet the growing demand without compromising timely patient care?
Possible solutions may include expanding surgical center capacity, optimizing OR scheduling with advanced analytics, or rethinking care delivery models to balance surgeon workload and patient access.
- Koushan M, Wood LC, Greatbanks R. Evaluating factors associated with the cancellation and delay of elective surgical procedures: systematic review. Int J Qual Health Care. 2021;33(2):mzab092. doi:10.1093/intqhc/mzab092.
- Smith JB, Bishi H, Wang C, Asopa V, Field RE, Sochart D. The accuracy and reliability of preoperative digital 2D templating in prosthesis size prediction in uncemented versus cemented total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review & meta-analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(11):1020-1039. doi:10.1302/2058-5241.6.210048.
- Bishi H, Smith JB, Asopa V, Field RE, Wang C, Sochart D. Comparison of the accuracy of 2D and 3D templating methods for planning primary total hip replacement: a systematic review & meta-analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2022;7(1):70-83. doi:10.1530/EOR-21-0060.
- Delayed and cancelled orthopaedic surgery: Causes and consequences. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(5):e14092. doi:10.1111/ijcp.14092.
- Accuracy of Preoperative 3D vs 2D Digital Templating for Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty. Arthroplasty Today. 2023;19:101165. doi:10.1016/j.artd.2023.101165.
- McCall M, Peebles M, Sandiford NA. Cancellation of elective orthopaedic procedures is not a benign practice and is often preventable. N Z Med J. 2021;134(1546):11-21.
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. Projected Volume of Primary Total Joint Arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(17):1455-1460. doi:10.2106/JBJS.17.01617
