Cyrus Morrison, MPH, CSCS
Data Analyst | DocSpera
Over the past several years, healthcare has significantly shifted from inpatient to outpatient surgical care, particularly in total joint replacement procedures, including knee, hip, and shoulder arthroplasty. This transition reflects a broader trend toward more patient-centered, cost-effective surgical approaches. At the same time, improvements in anesthesia and postoperative pain management have made same-day discharge increasingly feasible. Additionally, healthcare policy changes, such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) removing total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and total hip arthroplasty (THA) from the inpatient-only list, have accelerated the migration toward outpatient settings1. The expansion and specialization of outpatient Surgery Centers have provided infrastructure tailored to high-efficiency, high-volume orthopedic procedures.
In an analysis from January 2023 to June 2025 using DocSpera data, involving 123,299 joint replacement cases performed by 241 high-volume surgeons, we examined how outpatient procedures have evolved and what patterns have emerged.
Cumulatively, around 53% of these surgeries were performed in outpatient settings. This shift is not only substantial but remarkably consistent over time. Monthly variations showed that outpatient procedures typically ranged between 52% and 55%, with the highest percentage observed in December, where outpatient cases peaked at 57.3%. November showed the lowest, at 48.0%, highlighting the seasonal influence. Furthermore, a larger deviation was reported in the first six months of each year, with a tightening up in the second half (excluding November).
A closer examination of the data, using linear regression, revealed a gradual yet steady increase in the proportion of outpatient procedures over time. The rate of change was about 0.2 percentage points per month, a statistically significant trend with a p-value < 0.01. This suggests a significant and consistent shift toward outpatient care over time.
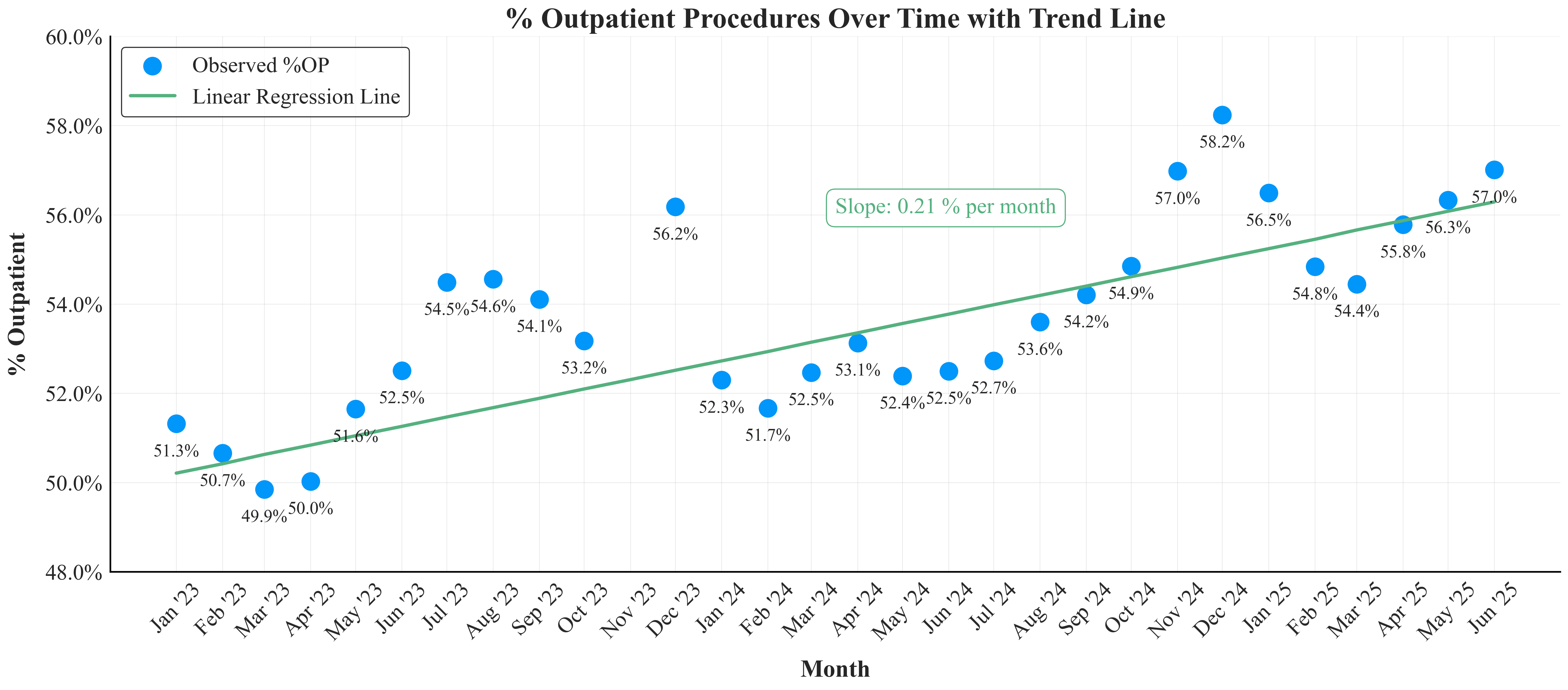
Seasonal patterns also became evident. While December showed the highest consistency in outpatient volumes with minimal variability, November stood out for its considerable fluctuation, likely influenced by external factors such as insurance cycles, holiday scheduling, and patient preferences. Understanding these seasonal dynamics can help healthcare systems plan more effectively for peak and off-peak periods.
Beyond averages, the distribution of outpatient procedure percentages illustrated essential nuances. An overall analysis revealed a moderately tight spread around the median, indicating relative stability across the study period. However, a month-by-month comparison showed more pronounced seasonal trends. Months like August and September exhibited little to no variability, while November’s marked fluctuation underscored how operational dynamics shift throughout the year.
Our findings align with broader national trends: a study published by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery found that outpatient orthopedic surgeries among Medicare patients have increased annually by approximately 8.8% since 20122. Similarly, a large-scale study of Medicare claims from 2019 to 2022 found a growing adoption of outpatient total joint arthroplasty (TJA), including among patients with more comorbidities, indicating broader patient eligibility for outpatient care3. Furthermore, projections suggest that by 2026, over 50% of same-day discharge TJA procedures will occur in outpatient settings, underscoring the direction of preference for outpatient facilities and the broader shift in facility planning strategies4. These consistent findings support the nationwide movement toward outpatient joint replacement surgeries.
In conclusion, this analysis confirms that outpatient surgical care for joint replacements is becoming increasingly prevalent and is subject to identifiable seasonal trends. These insights are highly valuable for healthcare administrators, surgical centers, and policymakers planning resource allocation, scheduling, and strategic operational decisions. With outpatient procedures rising, healthcare systems should consider adjusting staffing models, expanding outpatient facility capacity, and refining patient scheduling practices to align with these predictable trends.
- ASC Focus. New research shows rapid shift of total joint surgeries to outpatient. ASC Focus. 2023. Accessed June 13, 2025. https://www.ascfocus.org/ascfocus/content/articles-content/articles/2023/digital-debut/new-research-shows-rapid-shift-of-total-joint-surgeries-to-outpatient
- Malik AT, Quatman CE, Phieffer LS, Ly TV, Khan SN. Outpatient total hip and knee arthroplasty have comparable early outcomes with inpatient procedures in the Medicare population. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(22):1933-1938. doi:10.2106/JBJS.20.01105
- Penn State. Trends in the adoption of outpatient joint arthroplasties and patient characteristics. Penn State University. Published 2023. Accessed June 13, 2025. https://journals.lww.com/jaaos/abstract/2024/08010/trends_in_the_adoption_of_outpatient_joint.8.aspx
- The Journal of Arthroplasty. Advanced concepts in outpatient joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2024. Accessed June 13, 2025.https://www.arthroplastyjournal.org/article/S0883-5403%2824%2900114-1/fulltext
